Imagine using your office computer, which has all your necessary data for your business. You're going through the day like usual, but suddenly you can't access any of your critical files on your computer. All the files have become encrypted, and someone is asking on your screen to pay the ransom through crypto! Now, what do you do?
Ransomware: a name widely feared by tech enthusiasts. But why is it still a problem in 2022? Many types of security software are available; they should suffice to fight ransomware... shouldn't they?
First, you need to know that no one is 100% safe from malware attacks, and sophisticated attacks can exploit even the most robust ransomware protection software. But, if you are cautious and thoughtful when using the internet, your chance of being one of the ransomware victims will lessen drastically.
So, let's learn about malicious software, ransomware variants, successful ransomware attacks, and what you can do to protect yourself.
What Is Ransomware?
You can probably guess what ransomware is from its name. Ransomware is malware software that tries to obtain or encrypt data and block access to files. The program holds the user's data to ransom and the user can't access encrypted files. Any data or devices can be kept hostage using encryption technology. Cybercriminals then demand ransom money for the decryption key.
While ransomware has existed for some years, ransomware varieties are proving increasingly sophisticated in their capacity to spread, escape detection, encryption, or coercion, as seen in recent ransomware attacks.
Encrypting ransomware is designed to spread without getting detected by the system firewall or cybersecurity. So, it can very quickly be distributed through an organization's network, targeting servers and databases to encrypt files and sensitive data. Ransomware attacks can easily penetrate and paralyse an organization.
A ransomware attack on a business costs more than just money
Small and medium-sized businesses are often the targets of the most damaging ransomware attacks, as they can lack strong security. Ransomware attacks usually result in total losses reaching hundreds or thousands of dollars.
Short-term consequences can include disrupting critical business operations due to the inability to access data, costs associated with incident response, and mitigation efforts. Other consequences are interruption of system processes, fundamental infrastructure problems, lost productivity, and ransom payment if the organisation chooses to comply with the extortion demand.
Longer-term consequences might include decreased net profit, brand reputation damage, the loss of key executives and staff layoffs, the loss of consumers and partner companies, and – in some instances – the business's sustainability.
Which Industries are most likely to be victims of ransomware infection?
Ransomware is not a danger that exclusively affects particular businesses but is industry neutral. This Implies that, like other financially driven cyber attacks, the focus of most ransomware groups is on the opportunity to benefit rapidly from the exploitation of a business network and less on the features of the target firm itself.
This is reflected in our data, since no one industry significantly outnumbers others in attack volume. However, one out of every five ransomware victims worked in the manufacturing industry, which seems to be a favourite target of business email compromise (BEC) assaults due to the high volume of large invoices and international payments. Retail, wholesale, business services, construction, and healthcare round out the top five most hit industries.
Looking at the trends among victims, it is evident that malicious actors will exploit anybody they can—regardless of industry, organisation size, or location. All companies should be aware of the potential hazard.
What happens when a ransomware attack occurs?
To prevent ransomware attacks, you need to know the anatomy of one - the sequence of events that typically occur and the actions businesses should take to ensure a responsible and successful response.
Depending on the ransomware variant attack vector of a ransomware attack follows:
- A first attack is executed, allowing access to infected users' systems and mobile devices. The attack can be performed by phishing emails, remote desktop protocol, zero-day vulnerabilities, or other means that include one or more individuals unknowingly installing malware into the operating system. Clicking on emails with malicious attachments or links delivered from unknown sources is an everyday event for an unsuspecting user.
- Malware designed more aggressively, such as NotPetya, WannaCry ransomware exploits security vulnerabilities to infect machines without the need to trick users. Once the ransomware has seized control of the victim's computer, it encrypts files of the infected device. This step means the organization has been penetrated, regardless of how ransomware carried out the attack.
- Attackers deliver ransomware as a service to gain access to a device and lock and encrypt the victim's files afterward. Crypto ransomware is meant to encrypt information on gadgets, making any sensitive data and the systems that rely on them inaccessible.
- Once networks halt via encryption of crypto-ransomware or another mechanism, the infected computer shows a ransom note that says if the victim pays ransom, he will receive a private key to decrypt data. Attack vectors often include threatening with double extortion to create a feeling of urgency. Ransom demands are commonly asked in difficult-to-trace digital currencies such as Bitcoin.
What should you do if you're the victim of a ransomware attack?
If your company seems to be the victim of a ransomware attack, you should take action to ensure the maximum possible recovery:
- First, you need to try and identify the source of the infection and disconnect that computer or device from the rest of the network. This may be done simply by unplugging the computer from the web, including Wi-Fi and any storage devices, because there may be several infected computers in this infected system. It is wise to treat all devices as infected to prevent ransomware from spreading.
- The next step is to analyze what kind of ransomware variant is threatening your systems and check if any decryption tools are available. Do this by checking ransomware variants recognition websites or by seeking the help of information and technology professionals. Whatever approach you choose to detect the locker ransomware, it is essential to inform the local law enforcement. The FBI advises victims to report any ransomware attacks so that government agencies may improve quality efforts to prevent and capture ransomware attackers.
The simplest option to recover from a ransomware attack is restoring your folders and files from a backup if you recently backed up your data. Then, check to verify it was unaffected by the attack.
But sometimes you are not lucky enough. Ransomware authors often make ransomware variants that halt backup and restore capability. You may face a situation where your backups are corrupted or don't have any backup. If you find yourself in this situation, you may think that your only option is to pay the money. However, as previously said, you should not do this.
Many organizations have attempted this before with no results. After all, you're dealing with cyber criminals, so don't put your trust in anything. If you're lucky, a decryptor for the specific strain of ransomware you've been infected with may already be available. A list of decryptors is available at www.nomoreransom.org.
It is always ideal to have a dependable IT specialist on hand to assist you in navigating a scenario like this. They will suggest and guide you throughout the process.
Steps Your Business Can Take To Avoid Being Attacked
As cyber-attacks and data leaks increase, choosing a counter-attack strategy for your business is no longer viable. Instead, organizations must be prepared and responsible for safeguarding themselves against cyberattacks. Here's how it fits:
Understanding The Risks
Properly safeguarding your business against a cyber-attack begins with a thorough awareness of your company's information and external vulnerabilities when it comes to cybercriminals. You'll want to keep an eye out for methods a hacker may obtain access to your system by identifying areas of weakness.
The easy way is to educate yourself on the different cyber fraud schemes and challenges businesses face, such as phishing emails, ransomware, malware, and system hacking. Windows operating systems are prone to these problems. So be cautious before installing malicious programs because they may contain malware or ransomware.
Although it doesn't make anything impenetrable, you can take some small steps to make it harder for the attackers,
- Training the employees
- Proper Password management
- Two factor and biometric authentication
- Keeping system and software Up to date
Data Encryption
Today's hackers look for ordinary company-held information frequently left around, such as bank routing codes and employee social security numbers. Companies that store sensitive information should ensure that this information is constantly encrypted. Keep your data safe using full-disk encryption tools included with most operating systems.
It might take as much as a minute to enable the encryption on these devices, which will encrypt every file on your storage without slowing things down. Using this function, however, requires a little extra care.
The encryption will only be activated when no login is present. For cybercriminals, all they need now is an employee to take a little break and go over to the office kitchen to infect a machine with viruses and malware. To ensure that your precautions are enforced, configure your devices to automatically log off just after five to 10 minutes of inactivity.
These encryption measures are critical because, in the worst-case situation, hackers have been known to seize this data and encrypt it own. Often attacker threatens to leak data if the ransom is not paid. You won't face this if you have encrypted data in your system in the first place.
Data Backups
You should take the same steps regarding data backup. You can use this backup data in case the original data or primary copy is lost or somehow damaged by malware or ransomware. There are many cloud backup options for small businesses, and you can take advantage of them and won't be affected by malware or ransomware.
Regular backups are the only way to safeguard your small businesses from losing valuable data. Keeping the backup files stored separately is the best way to save them from malware or ransomware attacks.
Ensuring Hardware Security
Cyber-attacks are not always carried out using a computer system. Ensure your network systems are effectively locked down to ensure that no one gets away with sensitive information saved on your office PCs.
Most laptops and desktops include Kensington lock ports, which have a tiny loop that locks a device connected to a desk. Of course, they aren't entirely invisible to a thief, but their presence will demand more time and effort as they attempt to get away with your valuables. It could be enough to keep them from stealing in the first place.
Increase the security of your server room by ensuring workers keep the doors closed and secured. TA few organizations safeguard servers with locks, USB security keys, and hardware-based encryption, making it even more difficult for criminals to take and escape. Furthermore, cloud computing software enables companies to track down hijacked mobile laptops, smartphones, and even desktops.
Check Current System Security Status
Many IT professionals will evaluate your current network system and suggest the necessary security upgrades. They will help by checking your system's vulnerability and loopholes that a hacker might exploit via ransomware.
They will find these spots and fix them for you. You hire them to evaluate and upgrade your systems, which might be handy in the future.
Outsource your IT and security
If your company has few people, you should choose a professional IT services provider with full-time monitoring capabilities.
You may not consider the potential of cyber-attacks daily, but the consequences may be severe when one occurs. By ensuring that you have the basic security precautions today, you can avoid unnecessary troubles.
Should You Pay Ransomware Attackers?
Whether you should pay the ransom or not is a difficult choice that should be taken by the management board, not by security and risk managers. It will help you if you consider the consequences in both scenarios. What if we pay and don't pay the ransom?
What Happens If you pay?
If businesses pay the money, the attackers will send a decryption key and stop threatening to disclose stolen information. Payment, however, does not ensure that you can recover all data. The following are some of the facts about ransomware that management should consider:
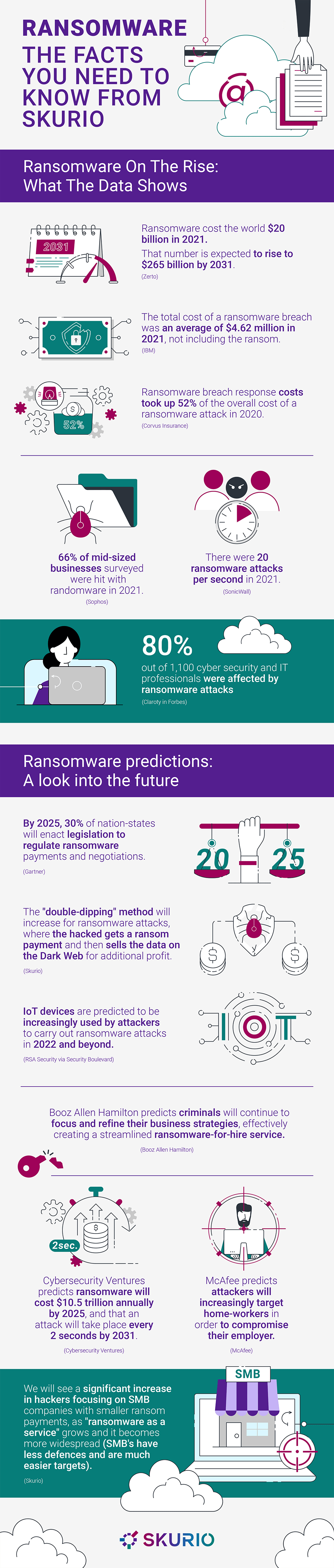
Analyzing the most significant ransomware attacks, only 65% of data is recoverable on average, and only 8% of companies can recover all their data. Files that have been encrypted by malware and ransomware are often unrecoverable. Decrypters given by the attacker may fail.
Sometimes you may need to develop a new decryption tool using keys extracted from the attacker's device. Data recovery can take weeks, especially if a considerable quantity of material has been encrypted. There is no certainty that hackers will delete the stolen data. If the information is valuable, they may sell or expose it later.
Things to watch out for in 2022
Double Dipping: What happens if you don't pay?
If you choose not to pay the attackers, they may use the Double Extortion or double-dipping method, where they steal sensitive information and threaten to reveal it publicly if the ransom is not fulfilled. This means that the target is still on the line for the ransom, whether or not data backups were used as a precaution.
Some ransomware operators have recently developed new Double Extortion techniques to boost the chance of receiving their ransom demand.
For example, in April 2021, experts reported that the DarkSide crime syndicate was using ransomware as a service to put extra pressure on their targets by threatening to provide stock traders with insider information based on exfiltrated data so they could take short positions against the stock exchange if they refused to pay the ransom demand.
Ransomware-as-Service adopted by criminal gangs
Ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) operators will never be legitimate businesses, but this has not stopped them from copying the organizational structure of standard corporations. Some criminal gangs, most notably the LockBit Gang, are contributing to the wider spread activity of ransomware infection.
Ransomware has become a global, billion-dollar industry. That's not surprising, as the average ransom estimates reach shocking new heights - valued at $1 million to $2 million dollars per payout. With this much money at stake, the most notorious criminal gangs have adopted RAAS, causing the wider spread activity of ransomware attacks in 2022. '
In fact, criminal gangs have even adopted professional structures for more efficient operations - including hiring contractors through legitimate job portal sites (who usually aren’t aware they are working for criminals) and setting up internal HR departments for easier and seemingly more genuine ransomware infection.
Automation techniques and RaaS will cause smaller companies to be hit
A new survey by Arcserve of 1000 IT decision-makers at small and midsize companies across India, found that 63% had been targeted by a ransomware attack, with 67% asked to pay over ‘$10k – $100k in ransom, 17 % to pay between $100k – $1m and another 17% to pay in ‘$10m – $100m. These numbers are not expected to get any better soon.
Despite spending billions on cybersecurity tools, businesses are still under prepared for ransomware threats. Only around 18% of all respondents to the survey said they’re confident in their ability to recover lost data in the event of a ransomware attack. As a result, smaller businesses are even less prepared, causing cybercriminals to view them as easy targets. Companies, especially those smaller, need to be vigilant when preparing for ransomware spreading in 2022.
Remote working is making ransomware easier to pull off
Since the onset of the global pandemic in 2020, unique working conditions were adopted across the world - including a huge number of employees having to work from home. Cybercriminals knew this, which is why attacks have become much more effective in the last 2 years. As remote and hybrid working seems to be here to stay, these attacks on remote workers are not likely to disappear soon.
For many workers, the pandemic would have been their first experience working from home, which means they might not be used to certain cybersecurity warnings or know the extent of what it takes to stay safe online. Workers may also only have one laptop, which means they will use the computer for personal activities like shopping, social media, or watching TV shows. As a result, cybercriminals can often launch phishing attacks against personal email addresses, which, if opened on the right device, can provide access to a corporate network.
Final thoughts
The takeaways are simple: regardless of area, industry vertical, or company size, a successful ransomware attack has a significant impact on both the top and bottom lines.
Ransomware attacks may have far-reaching consequences that can disrupt a company's core. In the worst-case circumstances, the result is often reputational harm, job loss, income loss, and even the eventual collapse of the firm itself.
Data backup solutions are also highly recommended. They may help ease some of the stress of recovery attempts after a ransomware attack.
However, businesses must remember that attackers have malware and ransomware variants that can make backups almost useless in some situations. Similarly, having the correct level of cyber insurance might help you recover from any damage.
Organizations must ensure that they have the right personnel with the required skill sets and security solutions to make sure that malware and ransomware attacks are blocked outright by effective security solutions. Or at least so malware and ransomware are detected early on and resolved before severe damage is done to the business.